Skidaway Island State Park
Despite what you see in cartoons, not all park rangers say, “Hey, Boo-Boo!” Luckily, one of ours does. You’ll want to meet her, along with the other rangers who help maintain this beautiful state park located just outside of Savannah. Not only is it a great place to get away for a few days, it’s also a great place for Teachable Moments, as we go well over our quota on this barrier island!
Skidaway Island State Park
Despite what you see in cartoons, not all park rangers say, “Hey, Boo-Boo!” Luckily, one of ours does. You’ll want to meet her, along with the other rangers who help maintain this beautiful state park located just outside of Savannah. Not only is it a great place to get away for a few days, it’s also a great place for Teachable Moments, as we go well over our quota on this barrier island!
Science
Develop a model to describe the roles of producers, consumers, and decomposers in a community.
Develop simple models to illustrate the flow of energy through a food web/food chain beginning with sunlight and including producers, consumers, and decomposers.
Design a scenario to demonstrate the effect of a change on an ecosystem.
Use printed and digital data to develop a model illustrating and describing changes to the flow of energy in an ecosystem when plants or animals become scarce, extinct or over-abundant.
Ask questions to determine where water is located on Earth's surface (oceans, rivers, lakes, swamps, groundwater, aquifers, and ice) and communicate the relative proportion of water at each location.
Ask questions to identify and communicate, using graphs and maps, the composition, location, and subsurface topography of the world's oceans.
Analyze and interpret data to create graphic representations of the causes and effects of waves, currents, and tides in Earth's systems.
Ask questions to identify types of weathering, agents of erosion and transportation, and environments of deposition.
Construct an explanation for the patterns of interactions observed in different ecosystems in terms of the relationships among and between organisms and abiotic components of the ecosystem.
Develop a model to describe the cycling of matter and the flow of energy among biotic and abiotic components of an ecosystem.
Analyze and interpret data to provide evidence for how resource availability, disease, climate, and human activity affect individual organisms, populations, communities, and ecosystems.
Ask questions to gather and synthesize information from multiple sources to differentiate between Earth's major terrestrial biomes (i.e., tropical rain forest, savanna, temperate forest, desert, grassland, taiga, and tundra) and aquatic ecosystems (i.e., freshwater, estuaries, and marine).
Use mathematical representations to evaluate explanations of how natural selection leads to changes in specific traits of populations over successive generations.
Construct an explanation based on evidence that describes how genetic variation and environmental factors influence the probability of survival and reproduction of a species.
Analyze and interpret data for patterns in the fossil record that document the existence, diversity, and extinction of organisms and their relationships to modern organisms.
Plan and carry out investigations and analyze data to support explanations about factors affecting biodiversity and populations in ecosystems.
Develop and use models to analyze the cycling of matter and flow of energy within ecosystems through the processes of photosynthesis and respiration.
- Arranging components of a food web according to energy flow.
- Comparing the quantity of energy in the steps of an energy pyramid.
- Explaining the need for cycling of major biochemical elements (C, O, N, P, and H).
Construct explanations that predict an organism's ability to survive within changing environmental limits (e.g., temperature, pH, drought, fire).
Develop and use a model to compare and analyze the levels of biological organization including organisms, populations, communities, ecosystems, and biosphere.
Develop and use a model based on the Laws of Thermodynamics to predict energy transfers throughout an ecosystem (food chains, food webs, and trophic levels).
Plan and carry out an investigation of how chemical and physical properties impact aquatic biomes in Georgia.
Analyze and interpret data related to short-term and long-term natural cyclic fluctuations associated with climate change.
Construct explanations about the relationship between the quality of life and human impact on the environment in terms of population growth, education, and gross national product.
Social Studies
Locate major physical features of the United States: the Atlantic Coastal Plain, the Great Plains, the Continental Divide, the Gulf of Mexico, the Mississippi River, and the Great Lakes.
Locate key physical features of Georgia and explain their importance; include the Fall Line, Okefenokee Swamp, Appalachian Mountains, Chattahoochee and Savannah Rivers, and barrier islands.
Analyze the economic, political and environmental impacts associated with industrialization and natural resource management around the world (e.g., fracking, strip mining, building of dams and reservoirs, deforestation, sustainable development, and renewable vs. non renewable resources).
1. How could starting controlled fires in a park prevent future forest fires?
2. Why do we have an agency like the DNR to oversee our natural resources?
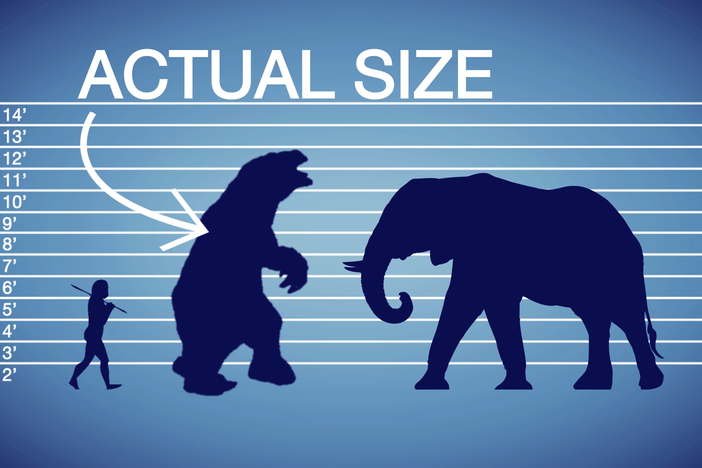
Giant Sloth: elephant-sized ground sloths native to South America that flourished until around 8,500 BC
Barrier Island: a long narrow island lying parallel and close to the mainland, protecting the mainland from erosion and storms
Fossil: something (such as a leaf, skeleton, or footprint) that is from a plant or animal which lived in ancient times and that you can see in some rocks
Estuary: an area where a river flows into the sea
Nutrients: a substance that plants, animals, and people need to live and grow
DNR: (Department of Natural Resources) a government agency that has statewide responsibilities for managing and conserving Georgia’s natural, cultural, and historical resources
Ecosystem: everything that exists in a particular environment
Naturalist: a person who studies plants and animals as they live in nature
Prescribed Fire: the process of planning and applying fire to a predetermined area, under specific environmental conditions, to achieve a desired outcome
Museum Curator: a content specialist charged with an institution's collections and involved with the interpretation of heritage material
-
Special Thanks
Holly Holdsworth, Kate Charron, Drew Klalo, Keith Clark, Kerry Nelson.
This content was developed under a grant from the U.S. Department of Education. However, this content does not necessarily represent the policy of the U.S. Department of Education, and you should not assume endorsement by the Federal Government.