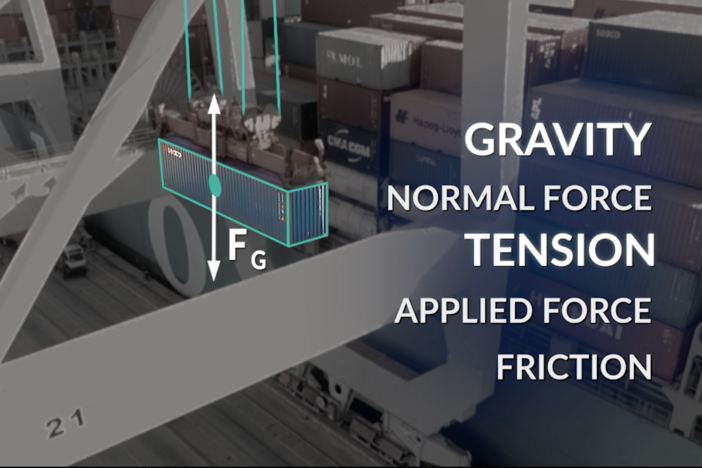
Segment E: Newton’s Third Law
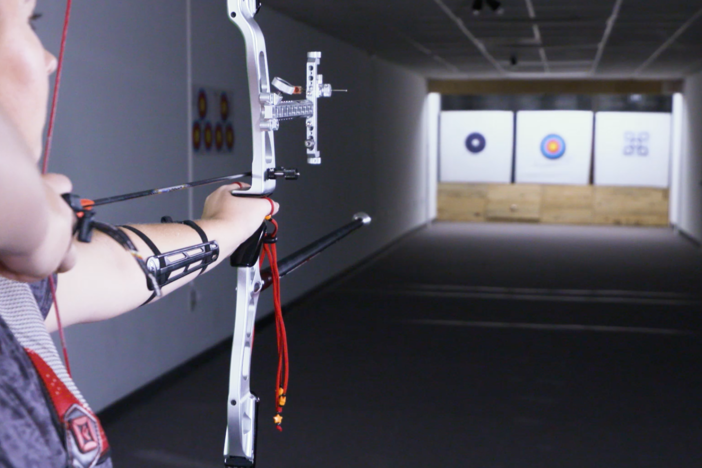
We head to an archery range in this segment to investigate Newton's third law.
Segment E: Newton’s Third Law
We head to an archery range in this segment to investigate Newton's third law.
Science
Obtain, evaluate, and communicate information about how forces affect the motion of objects.
Construct an explanation based on evidence using Newton's Laws of how forces affect the acceleration of a body.
- Explain and predict the motion of a body in absence of a force and when forces are applied using Newton's 1st Law (principle of inertia).
- Calculate the acceleration for an object using Newton's 2nd Law, including situations where multiple forces act together.
- Identify the pair of equal and opposite forces between two interacting bodies and relate their magnitudes and directions using Newton's 3rd Law.
Obtain, evaluate, and communicate information to explain the relationships among force, mass, and motion.
Construct an explanation based on experimental evidence to support the claims presented in Newton's three laws of motion.
Obtain, evaluate, and communicate information about cause and effect relationships between force, mass, and the motion of objects.
Construct an explanation using Newton's Laws of Motion to describe the effects of balanced and unbalanced forces on the motion of an object.
Construct an argument from evidence to support the claim that the amount of force needed to accelerate an object is proportional to its mass (inertia).
-Define Newton’s third law qualitatively and mathematically.
-Present examples of equal-and-opposite force action-reaction pairs.
-Introduce frames of reference and demonstrate their importance for understanding Newton’s third law.
-Clarify ways to think about systems of objects - either individually or in groups.
action-reaction pairs - pairs of objects in which one object exerts a force, known as the action, on another object, and the other object reacts to that action in a way in which the force is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction.
Newton’s 3rd Law of Motion - for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.
The Physics in Motion teacher toolkit provides instructions and answer keys for study questions, practice problems, labs for all seven units of study. GPB offers the teacher toolkit at no cost to Georgia educators.To order your teacher toolkit, complete and submit this form to request the teacher toolkit. You only need to submit this form one time to get materials for all seven units.