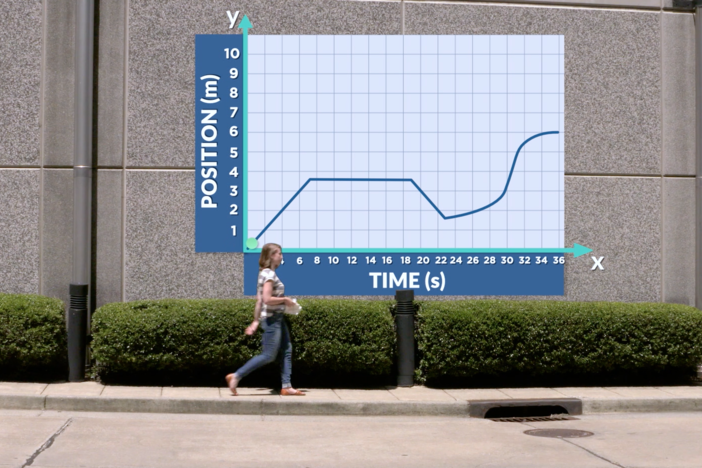
Segment B: Speed and Velocity
We head to the Porsche Experience Center Atlanta track to learn about the difference between speed and velocity. Different types of velocity are explored and we investigate how to find information from a position versus time graph.
Segment B: Speed and Velocity
We head to the Porsche Experience Center Atlanta track to learn about the difference between speed and velocity. Different types of velocity are explored and we investigate how to find information from a position versus time graph.
Science
Obtain, evaluate, and communicate information about the relationship between distance, displacement, speed, velocity, and acceleration as functions of time.
Plan and carry out an investigation of one-dimensional motion to calculate average and instantaneous speed and velocity.
- Analyze one-dimensional problems involving changes of direction, using algebraic signs to represent vector direction.
- Apply one-dimensional kinematic equations to situations with no acceleration, and positive, or negative constant acceleration.
Analyze and interpret data using created or obtained motion graphs to illustrate the relationships among position, velocity, and acceleration, as functions of time.
Ask questions to compare and contrast scalar and vector quantities.
Obtain, evaluate, and communicate information to explain the relationships among force, mass, and motion.
Plan and carry out an investigation to analyze the motion of an object using mathematical and graphical models.
-Compare and contrast speed and velocity.
-Differentiate between average velocity, constant velocity, and instantaneous velocity.
-Calculate average speed and average velocity.
-Find average velocity and instantaneous velocity values from a position versus time graph.
average speed - an object’s total distance traveled divided by the time elapsed. The SI unit is meters/second (m/s).
average velocity - an object’s displacement divided by time elapsed. The SI unit is meters/second (m/s).
constant velocity - velocity that remains unchanged.
displacement - an object’s overall change in position; the SI unit is the meter (m).
distance - is a measure of how far an object has traveled; the SI unit is the meter (m).
instantaneous velocity - the velocity of an object at a specific point in time.
The Physics in Motion teacher toolkit provides instructions and answer keys for study questions, practice problems, labs for all seven units of study. GPB offers the teacher toolkit at no cost to Georgia educators.To order your teacher toolkit, complete and submit this form to request the teacher toolkit. You only need to submit this form one time to get materials for all seven units.