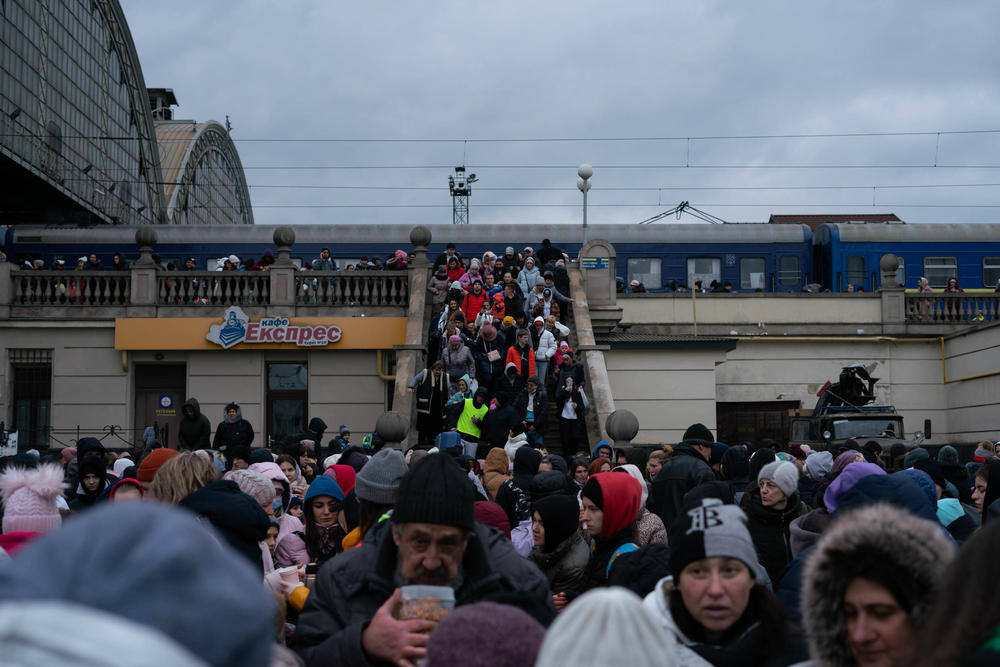Loading...
Section Branding
Header Content
6 key numbers that reveal the staggering impact of Russia's war in Ukraine
Primary Content
KYIV, Ukraine — Six months ago, Russia launched a full-scale invasion of neighboring Ukraine. The half-year mark comes on the same day — Aug. 24 — as a national holiday celebrating Ukraine's independence from the Soviet Union, an event in 1991 noted for its lack of bloodshed. Today the holiday takes on new meaning for many Ukrainians, as the country continues to fight in what it calls a new "war for independence."
Over the course of six months, the war has captured the world's attention, disrupted the global distribution of food and fuel and left the country reeling. To understand some of the war's impact on Ukraine, here are six key numbers:
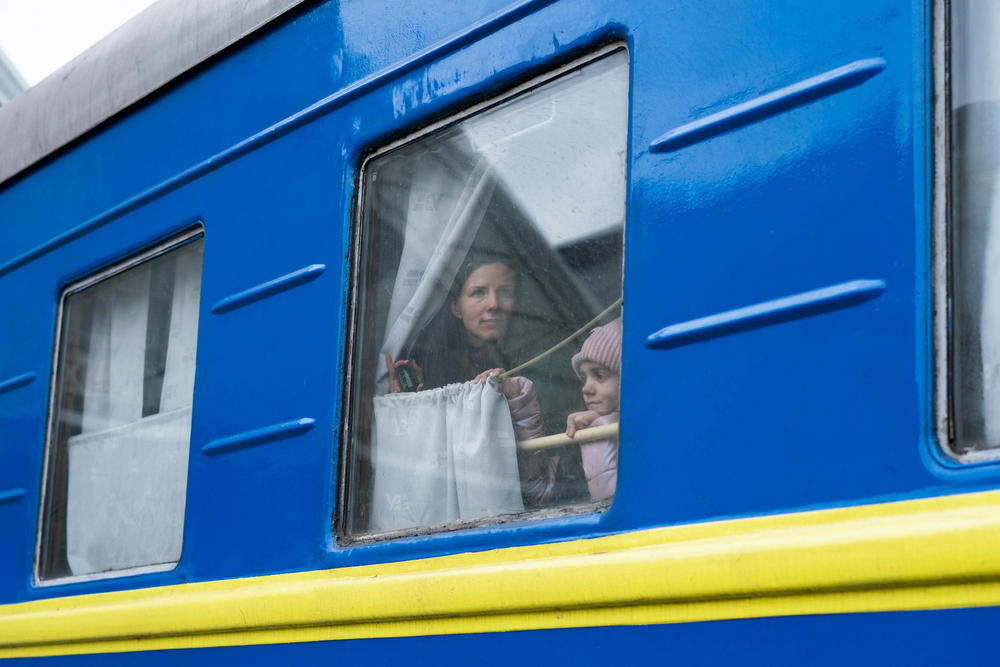
1. Over 13 million Ukrainians have been displaced
Russia's invasion of Ukraine has prompted Europe's largest refugee crisis since World War II. Since February, more than 13 million people have been forced to flee their homes, according to the United Nations refugee agency, UNHCR. Nearly 6.7 million refugees have dispersed across Europe, with Poland taking in the largest share. Another 6.6 million people are internally displaced within Ukraine.
Most Ukrainians who have fled the country are women and children, as the government has barred men ages 18 to 60 from leaving. The European Union's migration department says almost 500,000 Ukrainian children have been integrated into schools in EU countries.
Meanwhile, as the war has stretched on and shifted course, many Ukrainians are going back home. According to a survey by the International Organization for Migration, 5.5 million previously displaced people have returned home.
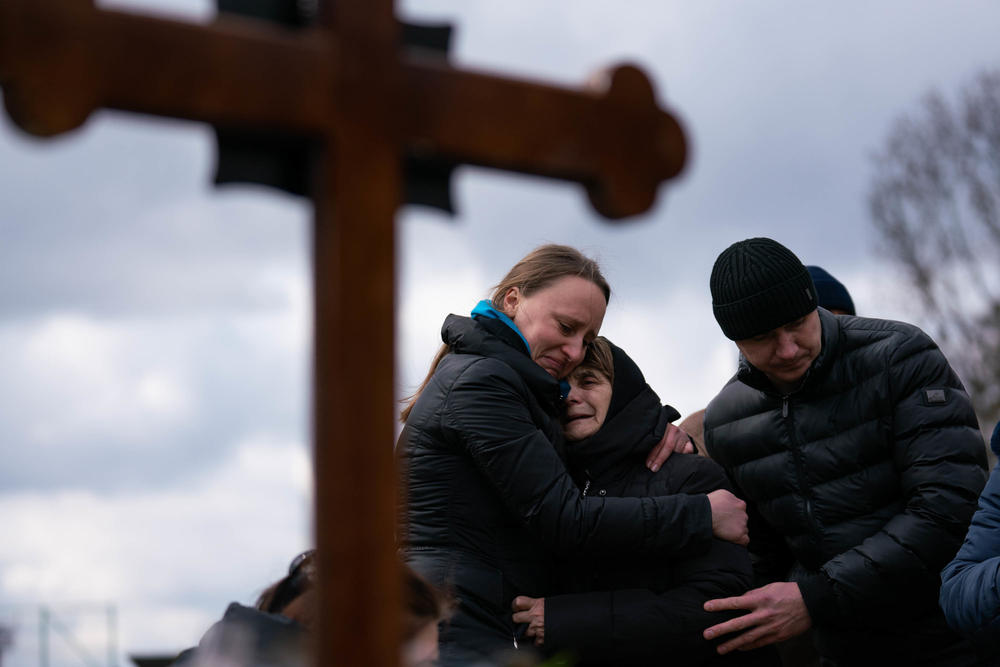
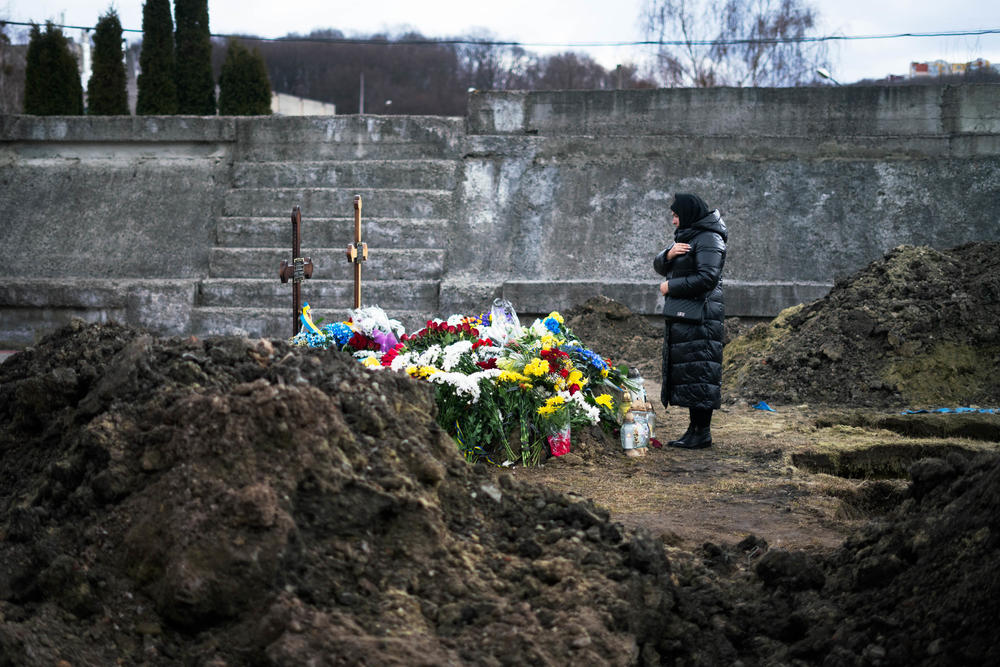
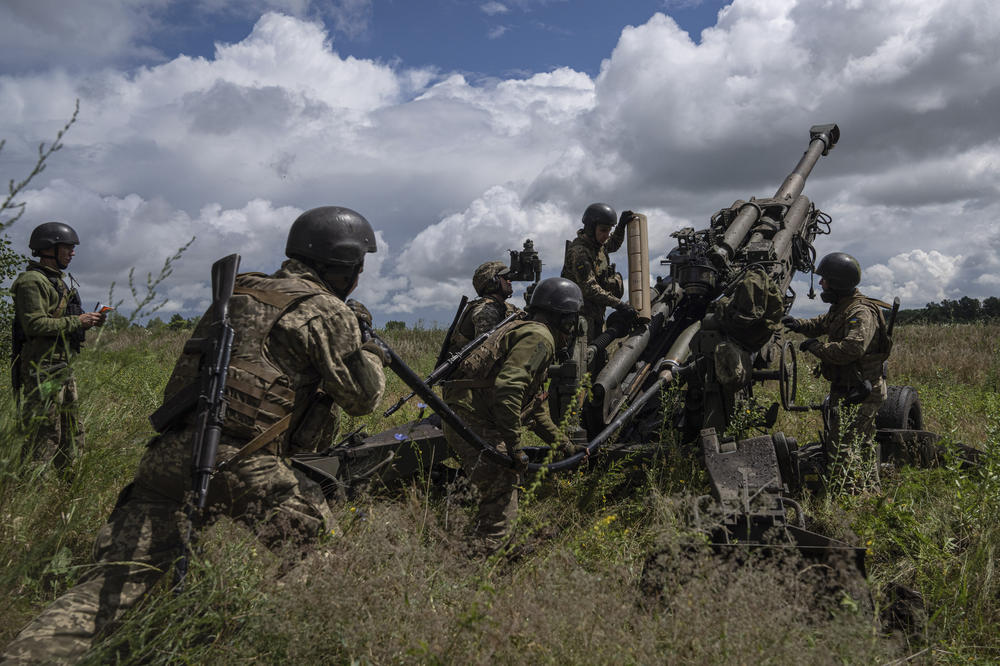
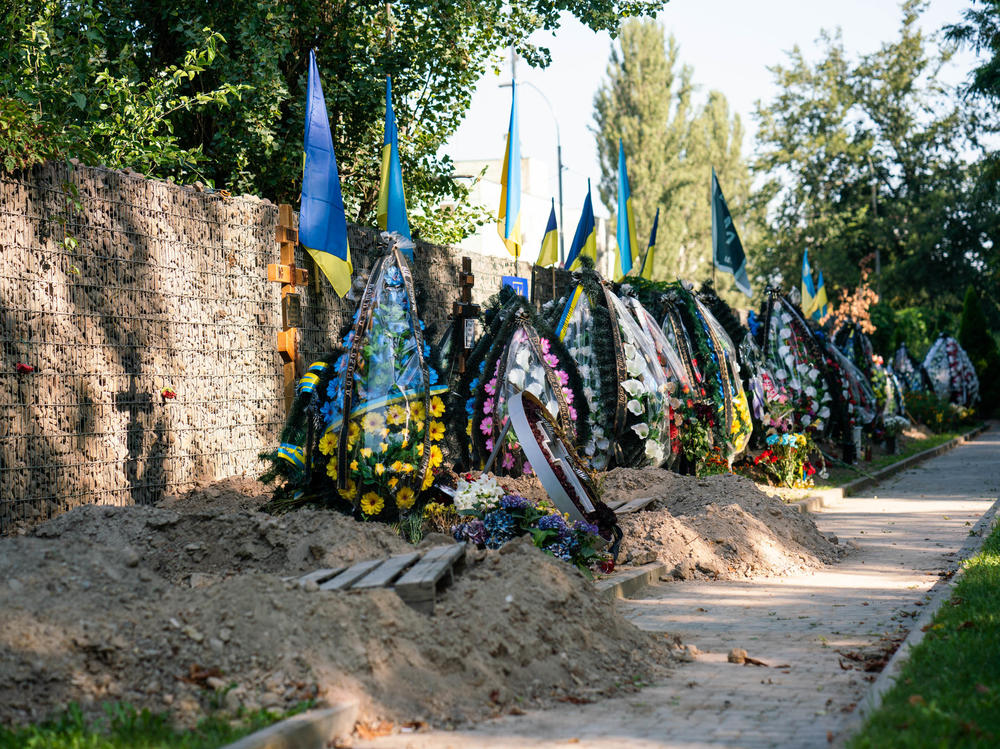
2. Tens of thousands of soldiers and civilians may have lost their lives in the war
Both sides have reported losing military personnel since the invasion began in February. Exact figures are hard to come by, since each country is reluctant to admit losses and often inflates the number of enemy fighters they've killed.
Gen. Valeriy Zaluzhny, commander-in-chief of the Ukrainian Armed forces, said this week at a public forum that Ukraine has lost 9,000 military personnel. The Ukrainian military has also claimed to have killed or wounded 45,200 Russian military personnel, with the largest losses in the eastern Donetsk and southern Mykolaiv regions.
Meanwhile, the U.N. human rights office has documented nearly 5,600 civilians killed in Ukraine during the conflict but believes the actual toll is much higher.
Russia has been releasing scant information on military casualties. Officials there said 1,351 of their own soldiers died in the first weeks of the war, in March, but have not released updated data since. Independent Russian news outlet iStories says it counted (through open-source information) more than 5,000 Russian service members killed, but that the true number could be higher.
In March, Russian military officials estimated Ukrainian losses at around 14,000 killed and 16,000 out of action.
3. Russia occupies 20% of Ukrainian land
In 2014, Russia invaded and annexed the Crimean Peninsula from Ukraine. Soon Russian-backed militants declared their intent to separate from Ukraine in the country's far east, launching a conflict that's been locked in a stalemate for nearly eight years.
In February, Russians controlled around 17,000 square miles of Ukrainian land, according to Ukraine's mission to the U.N. — Crimea being the size of Maryland and the self-proclaimed independent "republics" in Ukraine's east amounting to a territory about the size of New Jersey.
Six months into the full-scale invasion, Russia has expanded its territory in Ukraine almost threefold. In June, Ukraine's President Volodymyr Zelenskyy said Russia has occupied 20% of the country, or about 47,000 square miles. That's a territory about the size of New Hampshire, Vermont, Massachusetts, Connecticut, Rhode Island, New Jersey, Delaware and much of Maryland combined.
The line of contact between Russian and Ukrainian forces extends 570 miles, as of Monday.
4. Dozens of countries have pledged billions of dollars in military aid since the war began
Dozens of countries have supplied Ukraine with military assistance, including weapons systems and training. The bulk of the aid has come from the U.S. With President Biden's announcement Wednesday of another $3 billion, Washington has now committed $10.6 billion in security aid since Russia's February invasion. Billions more will be coming from an aid package passed in May.
On Ukrainian battlefields, Australia has become synonymous with the 88 armored vehicles it's provided, Turkey is known for its roughly 80 combat drones, Britain for the 22,000 soldiers it trained. Other countries have offered logistical support, like the 3.2 million gallons of diesel and jet fuel Slovakia provided.
When it comes to economic warfare, EU member states plus another 18 countries have levied individual sanctions against Russia in the past six months. But experts warn the sanctions could have a limited effect on Russia's export potential, as two-thirds of the world's population is concentrated in the countries that have either stayed neutral or supported Russia, according to the Economist Intelligence Unit.
5. Ukraine's economy could shrink by as much as 45% because of the invasion
The invasion has devastated Ukraine's economy across the board. The World Bank estimated in April that the Ukrainian economy could shrink by 45% this year. Last week, Ukraine's economy minister said the country's gross domestic product of $200.9 billion in 2021 is likely to contract between 35% and 40% by the end of the year.
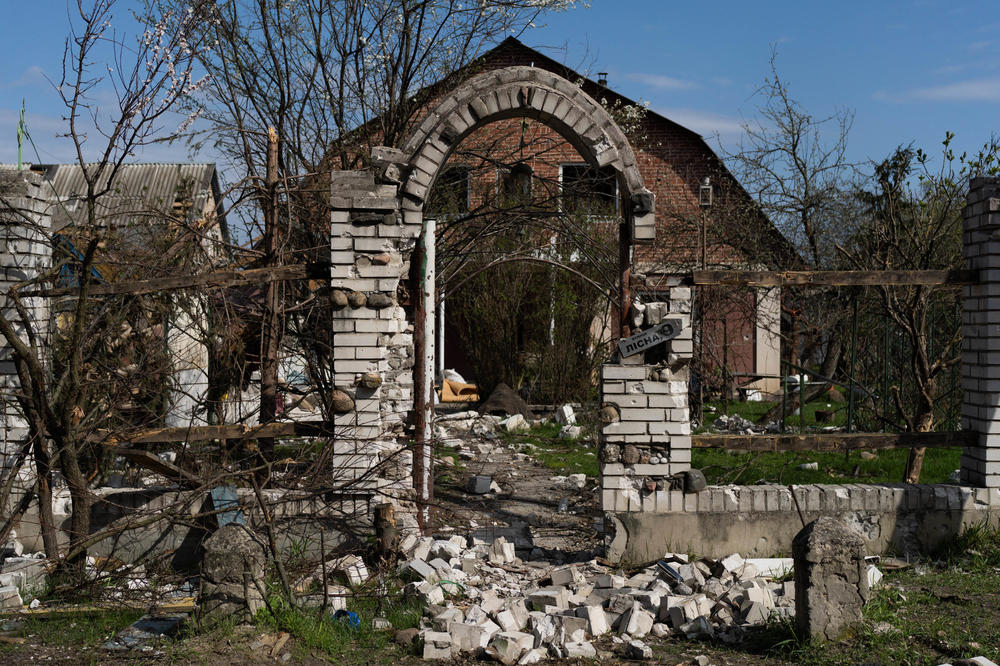
The conflict has cost Ukraine over $113.5 billion in damage, the Kyiv School of Economics says, with housing and transportation infrastructure hit particularly hard. KSE says the country will need upwards of $200 billion to recover.
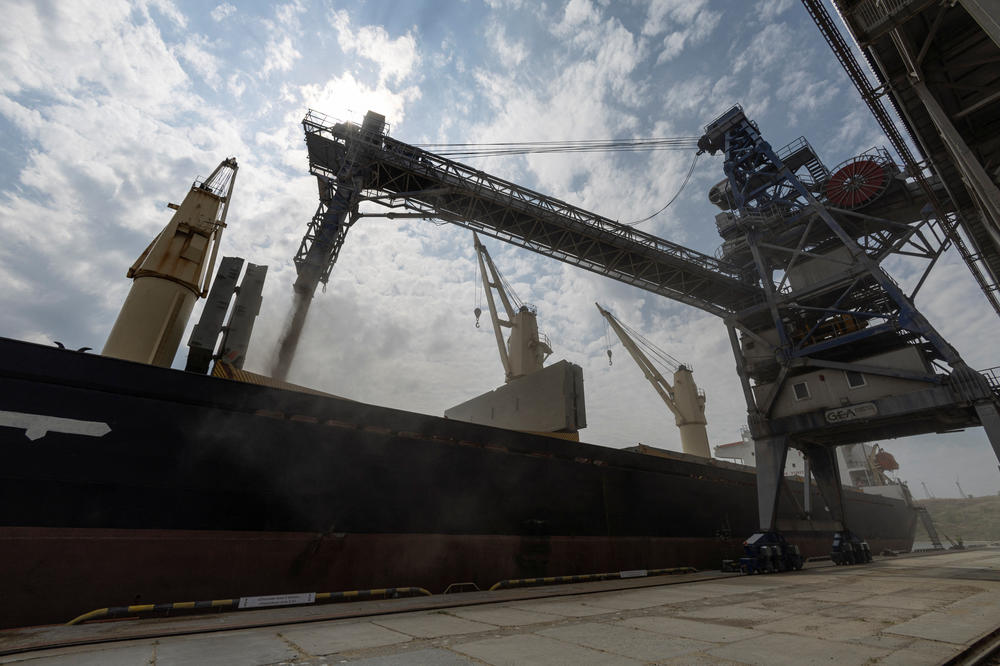
Meanwhile, Reuters reports that Ukraine's Agriculture Ministry says grain exports are down 46% from last year due to a five-month blockade of the country's Black Sea ports. And despite a U.N.-brokered deal reached in July to allow food shipments to depart Ukraine, the agriculture sector is still expected to take a huge hit. The country's steel industry has also taken a beating.
Ukraine has lots of friends throughout the world who are trying to help keep its economy afloat. The U.S. alone has already pledged $8.5 billion in financial assistance to Kyiv this year to keep government offices open and staffed and utilities working. Meanwhile, the European Union has given billions of euros to Ukraine since February, and has recently fashioned a package to give 8 billion euros more in financial aid over the next six months.
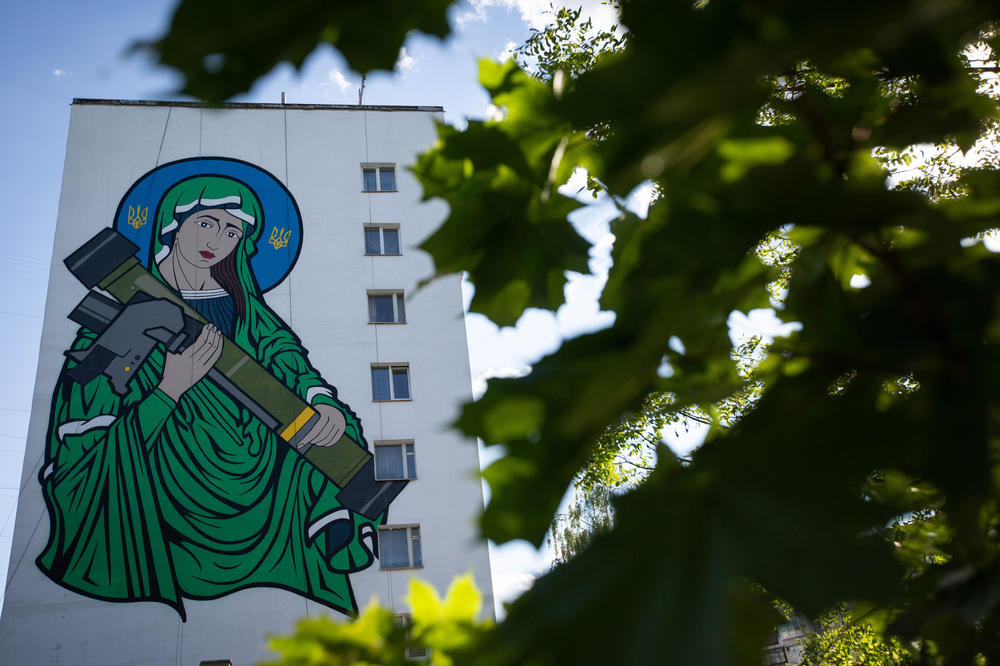
6. Bake sales, spare change and "St. Javelin" have raised over $500 million in private money to help Ukraine
In February, a Canadian-Ukrainian writer, Christian Borys, and California artist Chris Shaw created a meme of a woman appearing like the Virgin Mary holding a rocket launcher. Borys called it "St. Javelin," after the U.S.-supplied anti-tank missiles. Since then, he's formed the meme into a brand that has sold more than $3 million worth of stickers and other merchandise to help Ukraine.
Borys' initiative is one of hundreds like it.
In June, Ukrainian TV personality Serhiy Prytula asked his fans to buy him a Turkish-made drone priced at $5 million. He ended up raising $55 million. Baykar, the company that makes the drone, refused to take the money. Instead, the company donated three drones. In August, Prytula used the funds he raised to purchase a reconnaissance satellite for Ukrainian intelligence.
As of July, Ukraine's National Bank reports to have collected $530 million in donations for the Ukrainian military — mostly from people rounding up at shop cash registers and fundraisers in the country. On Tuesday, residents of the small western Ukrainian town of Dubno raised $866.55 at a bake sale and flea market for the military.
Julian Hayda reported from Kamianets-Podilskyi, Ashley Westerman from Lviv and Elissa Nadworny from Kyiv. Polina Lytvynova contributed to this report.
Copyright 2022 NPR. To see more, visit https://www.npr.org.